If your best content is buried three clicks deep, you’re losing rankings and revenue. Automated internal linking solves this fast—building topic clusters, accelerating discovery, and lifting the pages that matter most. In this guide, you’ll learn exactly how automation works, how to set safe linking policies, and how to launch in weeks (not quarters) with a practical, platform-agnostic playbook.
Why Automated Internal Linking Matters for Topic Clusters
Internal links are the connective tissue of topic clusters. Done right, they clarify relationships between pages, guide users across the journey, and distribute link equity to priority URLs. Automation unlocks this at scale—so every new article strengthens the whole cluster within hours, not months.
Multiple industry sources echo this: internal linking helps search engines understand site structure and relative importance, a key part of cluster SEO and topical authority. It’s a durable advantage that improves crawl efficiency and rankings across related queries.
Search Intent Alignment Through Clusters
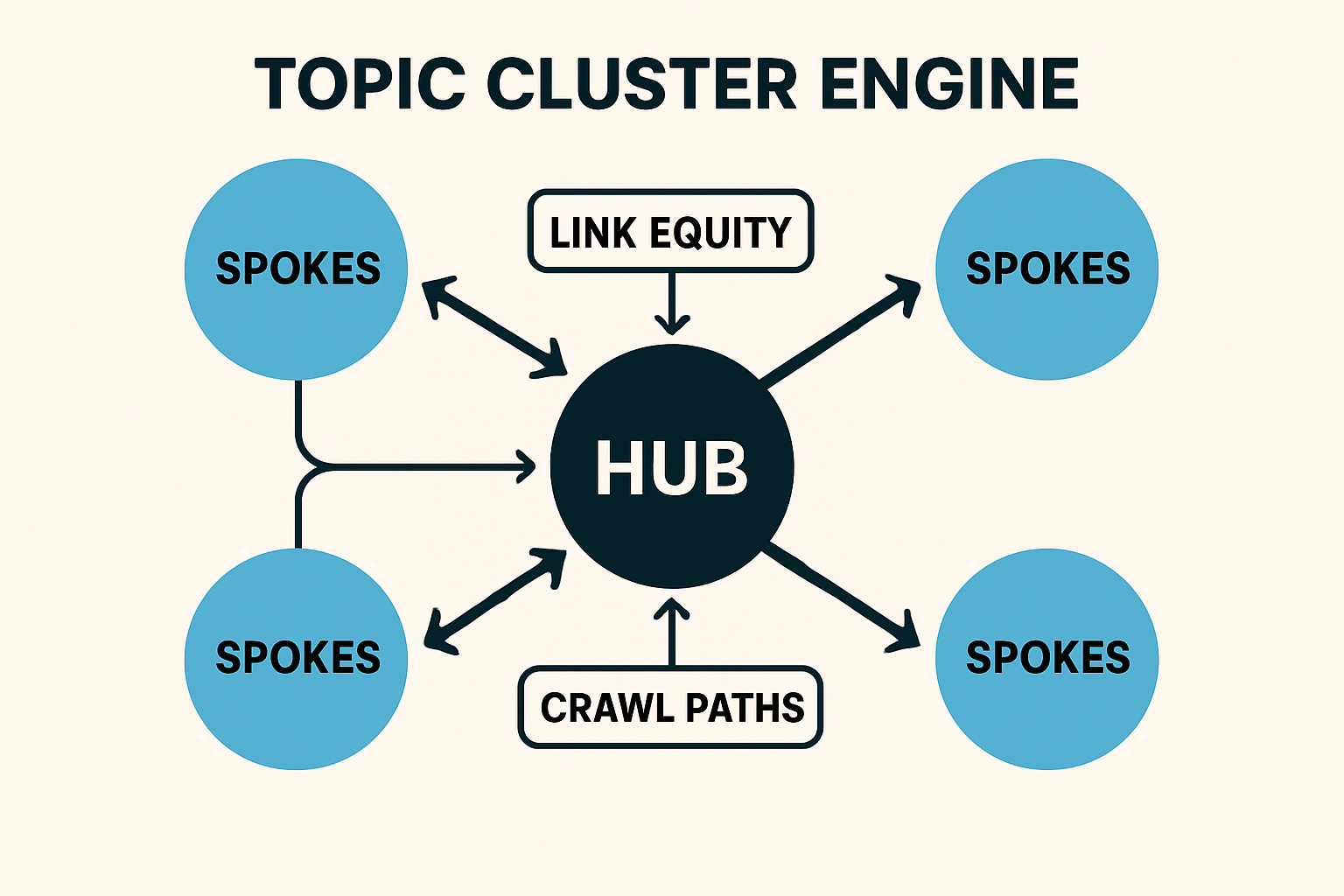
Clusters organize content around a hub-and-spoke model: a hub (or pillar) page summarizes the topic; spoke pages go deep on subtopics. Automated internal linking makes this model “clickable”—connecting user questions to the right depth at the right time.
Clarify intent: Link BOFU, MOFU, and TOFU content paths to match where users are in the journey.
Increase engagement: Contextual links to related spokes reduce pogo-sticking and keep users reading.
Reinforce themes: Consistent hub-spoke linking signals topical depth and relevance.
Crawl Efficiency and Equity Distribution
Automated internal linking reduces crawl depth and ensures high-value pages are discovered quickly and revisited more often. It also funnels PageRank-like equity from strong hubs to new or strategic spokes.
Shallower crawl paths: Bots find important URLs faster via hubs, breadcrumbs, and related modules.
Smarter equity flow: Rule-based internal links prioritize key URLs when equity is scarce.
Fewer orphans: Automation detects and links orphaned pages to their nearest relevant hubs.
Definition: Crawl efficiency is how quickly and completely search engines discover and refresh your content. Automated internal linking increases efficiency by flattening navigation and concentrating links on priority paths.
E-E-A-T and Topical Authority Signals
Topical authority is built when semantically related pages cross-support each other. Structured internal linking across entities and intents amplifies your expertise and makes relationships explicit for both users and crawlers.
Semantic coverage: Link pages that share entities, questions, and adjacent intents.
Expertise signals: Hubs curate sources, definitions, and methodologies; spokes provide deep execution.
Clear hierarchy: Hubs receive more internal links to signal importance, while spokes interlink laterally.
Further reading: Yoast explains how internal links reveal site structure and importance to search engines, supporting topic clusters and depth. Industry write-ups also show clusters improve crawl and ranking outcomes across related keywords.
How Automated Internal Linking Works
Modern automation blends a topic graph, rule engines, and semantic matchers. The result is a system that identifies where a link belongs, which anchor to use, and how to balance density across templates.
Topic Graphs, Entities, and Proximity
A topic graph maps entities (people, places, concepts, products) and their relationships. Semantic proximity—how closely two pages relate based on shared entities and intents—determines the most relevant internal link targets.
Entities: Core nodes like “internal linking,” “topic clusters,” “anchor text.”
Ontology/taxonomy: Parent-child relationships (pillar → hub → spoke).
Proximity: Overlap of entities and user intents drives link candidacy and priority.
Rule-Based Matchers and Pattern Libraries
Deterministic rules fire links when metadata or patterns match. These are precise, transparent, and easy to govern.
Metadata rules: If post.tag = “topic-cluster”, add link to pillar.
URL patterns: If path starts with /seo/topic-clusters/, recommend related spokes.
Regex/patterns: On match for “internal linking” in body, inject glossary link once per 500 words.
Module triggers: If template = blog, render “Related Articles” with same entity set.
AI/Embedding-Based Context Matching
For nuance, use embeddings and LLM prompts to score semantic similarity. Vector search proposes high-quality link pairs even when keywords differ (e.g., “site architecture” → “crawl paths”).
Generate embeddings for each URL and paragraph chunk.
Compute cosine similarity to hub/spoke vectors.
Threshold and rank candidates; assign anchors from an approved taxonomy.
Enforce caps per template; dedupe anchors per target.
Result: Highly relevant, low-maintenance links that adapt as your library grows.
Pre-Work: Audit and Map Your Clusters
Before turning on automation, build a clean cluster taxonomy, assign roles, and size opportunities. This prevents noisy links and ensures the right pages receive equity.
Inventory Content Into a Cluster Taxonomy
Group existing URLs by pillars, hubs, and spokes using tags and categories. Align to search intent (TOFU, MOFU, BOFU) to guide link direction and CTA placement.
Tag each post with entities and target intents.
Standardize URL structure for clusters.
Create one pillar per major topic; attach hubs and spokes.
Need structure help? Use this pillar page template to model your hubs and spokes.
Define Pillar, Hub, and Spoke Roles
Every page needs a role to determine link direction and priority. A simple hierarchy prevents cannibalization and leakage.
Pillar page: Receives most internal links; links down to hubs.
Hub page: Links up to pillar; links laterally and down to spokes.
Spoke page: Links up to hub; cross-links to adjacent spokes when relevant.
Gap Analysis and Prioritization
Identify missing spokes, thin hubs, and under-linked pages. Prioritize by search opportunity and cluster cohesion. For a fast start, run a keyword gap analysis to size demand and coverage.
Anchor Text Taxonomies and Linking Policies
Automation is only as good as its guardrails. A documented anchor taxonomy and policy keeps anchors natural, diverse, and safe from over-optimization.
Primary, Secondary, and Semantic Variant Anchors
Primary (exact/near-exact): Use on hubs/pillars, capped per template.
Secondary (partial/phrase): Use predominantly across body copy.
Semantic variants/synonyms: Rotate to cover related language and reduce footprints.
Placement and Frequency Rules
Intro: One contextual link if it clarifies scope.
Body: One link every 150–250 words, max X per section.
Modules: Related articles, breadcrumbs, and in-content blocks.
Footer: Avoid sitewide exact-match anchors.
Handling Duplicates, Cannibalization, and Nofollow
Duplicate anchors: Deduplicate per paragraph; rotate variants.
Cannibalization: Prefer the canonical target; add disambiguation anchors (e.g., “guide vs checklist”).
Nofollow: Use sparingly for legal or low-value pages; avoid nofollowing important internal pages.
Automation Approaches and Tooling
Choose the lightest-weight approach that meets your needs today and can scale tomorrow.
CMS-Level Auto-Linking Rules and Templates
Use CMS fields (tags, categories, entity lists) to drive module logic.
Shortcodes or template tags to render hub links, related lists, and glossary references.
Conditional logic per content type (blog vs documentation vs category pages).
Sitemaps, Breadcrumbs, and Related Blocks
Navigation modules reinforce cluster structure while helping users and bots traverse your content.
XML sitemaps: Ensure clusters are discoverable and updated promptly.
Breadcrumbs: Surface hierarchy and reduce crawl depth for deep pages.
Related articles: Auto-populate with entity/intent matches, not just shared tags.
Headless/API Pipelines for Scale
Middleware: Score and inject links during build or publish events.
Microservices: Vector similarity service proposes link pairs; rules engine validates.
CI/CD: Run link QA checks in pre-prod; ship with confidence.
Implementation Playbooks by Platform
Below are practical, non-proprietary patterns you can adapt across common platforms.
WordPress
Create a custom taxonomy for clusters; attach to posts and pages.
Use custom fields for entities/intents; render related links via theme hooks (e.g., in functions.php).
Add a reusable “Related Spokes” block filtered by cluster + entity overlap.
Shopify
Define metafields for entities, intents, and hub references.
In Liquid templates, populate in-content links and collection sidebars from those metafields.
Auto-link FAQs and guides from product pages to relevant how-tos and comparison spokes.
Webflow and Headless
Use Webflow CMS references and collection lists to surface related pieces in clusters.
For headless, use GraphQL to fetch link targets by entity similarity; inject during page build via webhooks.
Centralize anchor taxonomies in a repository consumed by the frontend at build time.
Workflow: Orchestrate Content and Links with SEOsolved
Internal linking automation accelerates when your content supply is consistent, structured, and aligned to clusters. That is where SEOsolved fits: it builds a prioritized cluster roadmap, generates in-depth articles, and outputs the metadata your linking rules need.
Generate a Cluster Roadmap with SEOsolved
SEOsolved analyzes competitors, discovers hundreds of ranking keywords, and outputs a prioritized plan with publishing cadence. You get pillars, hubs, and spoke ideas aligned to search intent—ready for your linking engine.
Explore how automation powers ROI in SEO automation software: ROI-rich benefits for content.
Create In-Depth Articles at Scale
High-quality, long-form content is the best substrate for internal links. SEOsolved generates SEO-optimized, source-backed articles that naturally include linkable sections, FAQs, and definitions.
Learn why semantic coverage matters in Semantic SEO: The Fast Track to Unshakable Authority, and how to produce consistently with Automated Content Creation: Scale SEO Fast in 2025.
Feed Metadata to Your Linking Rules
SEOsolved outputs categories, entities, and intent tags. Pipe these into your CMS fields or headless pipeline so your rules and vector matcher can trigger relevant internal links automatically.
Stat Ranking Today with a complete cluster plan and content ready for automated internal linking.
Quality Control and Guardrails
Scale without sacrificing UX. Establish sensible caps and rotation so internal links remain helpful and natural.
Link Quotas and Dampening
Cap links per template (e.g., 8–12 for long-form, 4–6 for short posts).
Throttle additions when a page exceeds a link density threshold.
Weight links by prominence; prefer in-body over boilerplate.
Anchor Rotation and Diversity
Maintain a synonym list for each target; rotate anchors across variants.
Avoid repeating the same anchor more than once per 300–500 words.
Refresh anchors quarterly as SERPs and terminology shift.
Exclusions and Negative Rules
Exclude legal, privacy, and thin utility pages from suggestions.
Protect conversion pages by limiting outbound links above the fold.
Honor robots directives and canonicalization policies in automation.
Measurement, Reporting, and Forecasting
Prove impact with clear KPIs and experiment design. Internal linking is measurable in weeks.
Core KPIs for Internal Linking
Orphan rate: Percentage of pages with zero internal inlinks.
Time-to-discovery: Days from publish to first bot visit/indexation.
Internal CTR: Clicks on in-content links per 100 sessions.
Assisted rankings: Query lift for pages receiving new inlinks.
Crawl depth: Average clicks from home to key pages.
Experiment Design and Incremental Tests
Select a cluster as treatment; hold back a similar cluster as control.
Ship automation to treatment only; monitor 4–8 weeks.
Compare discovery time, internal CTR, and ranking lift vs control.
Iterate thresholds, caps, and anchors; roll out broadly.
Crawl Budget and Log-File Monitoring
Use server logs or Search Console crawl stats to verify bots follow your new paths and revisit faster. Track crawl hits by URL depth and note improvements in coverage after automation.
Advanced Tactics for Topic Clusters
Once the basics are stable, add sophistication to squeeze more value from every link.
Semantic Proximity Scoring
Compute entity overlap and cosine similarity to prioritize link targets. Promote the top-scoring hub and two strongest spokes per page. This concentrates equity while keeping UX clean.
Stage-Based Linking Along the Funnel
Map links by funnel: TOFU explainer → MOFU comparison → BOFU case study. Use module rules to surface the next best piece for conversion paths.
Programmatic Sidebars and In-Content Blocks
Inject dynamic modules that update as clusters grow. Sidebars pull latest spokes; mid-article blocks surface related frameworks and checklists relevant to the current section.
Case Study Walkthrough (Hypothetical)
Here’s a realistic 90-day rollout for a mid-sized site with 500+ blog posts and emerging clusters.
Baseline Snapshot
Orphan rate: 18%
Average crawl depth to spoke: 3.2
Internal links per page (median): 6
Time-to-discovery for new posts: 5–7 days
90-Day Rollout and Results
Weeks 1–2: Map clusters, define roles, set anchor taxonomy.
Weeks 3–4: Turn on CMS rules, related blocks, and breadcrumbs.
Weeks 5–8: Enable vector matcher; add link caps and rotation.
Weeks 9–12: Iterate thresholds; add dynamic sidebars and hub boosts.
Expected deltas: faster discovery, more internal link clicks, and broader ranking coverage for cluster terms.
Key Lessons and Next Iterations
Start deterministic; add AI matching after you stabilize rules.
Guardrails matter—caps, rotation, and exclusions keep UX first.
Close content gaps in parallel to maximize cluster lift.
Templates and Checklists
Use these ready-to-adapt structures to speed implementation and governance.
Internal Linking Policy Template
Policy outline:
Goals: reduce orphan rate to <5%, cut discovery time by 50%.
Quotas: cap links per template; prioritize in-body links.
Anchors: primary/secondary/variants with rotation rules.
Exclusions: legal, pagination, low-value utility pages.
Monitoring: monthly audits; quarterly threshold reviews.
Anchor Taxonomy Spreadsheet Columns
Target URL
Target Title
Primary Anchor
Secondary Anchors
Semantic Variants/Synonyms
Intent (TOFU/MOFU/BOFU)
Cluster/Entity Tags
Max Uses Per Page
Go-Live QA Checklist
No broken links; anchors readable and natural.
Link density within caps; no duplicates in proximity.
Related modules render correct cluster items.
Analytics tracking internal link clicks.
Logs show bot traversal of new paths.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Stay proactive with monitoring and targeted rollbacks when needed.
Over-Linking Symptoms and Fixes
Symptoms: visual clutter, falling internal CTR, rising bounce.
Fixes: lower caps, increase anchor variety, prefer module links over inline.
Index Bloat and Faceted Navigation
Contain parameters with canonicals and robots directives.
Link to clean, canonical URLs from modules and body.
Avoid linking into infinite faceted spaces from hubs.
When to Pause or Roll Back Rules
Thresholds: internal CTR down >25% or crawl depth worsens.
Immediate pause: spikes in duplicate anchors or link loops.
Rollback plan: disable modules, revert to last stable config, re-test in staging.
Next Steps and CTA
Here’s a 30-day plan to go live with confidence and start capturing cluster lift.
Quick-Start Plan (First 30 Days)
Audit URLs; map clusters and roles; document anchor taxonomy.
Implement CMS rules for hubs, breadcrumbs, and related blocks.
Launch pilot on one cluster; set link caps and rotation.
Add embeddings matching; monitor KPIs and logs.
Iterate thresholds; expand to second cluster.
Team Roles and Ownership
SEO lead: Taxonomy, policies, KPIs, QA.
Content lead: Publishing cadence, upgrades.
Engineer: Rules engine, modules, CI/CD checks.
Analyst: Reporting, experiments, forecasting.
CTA: Stat Ranking Today (https://www.seosolved.com/)
Pair a prioritized cluster roadmap with in-depth content that your automation can link immediately. Stat Ranking Today with SEOsolved.
Also see: Pillar page template and Semantic SEO guide for cluster planning.
FAQ
What is automated internal linking?
It’s the use of rules and semantic matching to add relevant internal links across pages, at scale, without manual editing.
How many internal links per page is best?
Aim for natural density: 4–6 on short posts and 8–12 on long-form pages, prioritizing in-body links over boilerplate.
Will automation cause over-optimization?
Not with guardrails. Use anchor rotation, per-template caps, deduping, and exclusions to keep anchors natural.
Do internal links really help rankings?
Yes. Internal links signal hierarchy and topical relevance, helping search engines understand importance and relationships.
Where should I start?
Start with one cluster: define roles, set a simple anchor taxonomy, enable related modules, then expand with embeddings.
References and Further Reading
Internal linking clarifies site structure and importance: Yoast
Topic clusters drive domain-wide gains: Diffuse Digital Marketing
Clustering enhances topical authority and UX: Ranklytics
Hub-spoke internal linking forms a semantic web: Wellows
Best practices for internal linking and clusters: 6th Man Digital
Google on internal link signals via industry summary: AirOps
Programmatic SEO and orphan prevention: SEOmatic
HubSpot-cited uplift from topic clusters: Third Wunder