If your best pages are stuck on page two, your internal links are leaving money on the table. AI internal linking turns messy webs of content into structured pathways that pass authority, clarify intent, and lift the right URLs—fast. In this guide, you’ll get a 7‑step workflow, copy‑and‑paste prompts, and the exact tools to automate safely.
AI Internal Linking in 2026: Why It Works
Definition: AI internal linking is the use of NLP and LLMs to automatically propose and quality‑check contextual links between your own pages so crawlers and users find the best answer with the fewest clicks.
Internal links guide crawlers and users, distribute link equity, and signal topical relationships. Shorter click paths and stronger in‑content links improve indexation speed and ranking potential. Googlebot follows internal links to discover and prioritize pages; more internal link equity often equals higher perceived importance and faster indexing. See research on crawl depth, internal links, and indexation speed.
How internal links distribute authority and intent
Link equity flow: PageRank‑like signals pass through links. Contextual in‑body links carry strong semantic relevance and can outrank template links.
User intent routing: Links within paragraphs act as micro‑CTAs that move readers to the next best answer, reducing pogo‑sticking.
Crawl efficiency: Pages two to three clicks from the homepage are crawled and indexed more reliably and quickly, improving freshness and discovery.
How AI finds opportunities: entities, embeddings, similarity
Modern AI models use entity extraction and vector embeddings to measure semantic similarity between passages, not just keywords. This lets you match the exact sentence on a source page to the best target page and propose a natural anchor. For deeper background, see our primer on Semantic SEO and topical authority.
As AI search agents proliferate, a logical internal linking system helps both bots and humans traverse related content. Well‑organized internal links make your site more likely to be selected as a reliable source for AI answers, not just traditional SERPs (details).
Prerequisites: Inventory, Taxonomy, and Data Sources
Accurate AI suggestions depend on clean inputs. Create a structured dataset from your site, align it with real queries, and define clusters.
Crawl and export URLs, titles, H1–H2s, and word count
Use a site crawler to export: URL, title, H1/H2s, word count, publish date, canonical, status code, and current internal outlinks.
Pull a separate internal links report and click depth for each URL.
Normalize titles and slugs, dedupe near‑duplicates, and flag thin content.
Keep a “do‑not‑link” list (legal, checkout, paginated archives).
Pull queries and top pages from Google Search Console
Export pages with impressions/clicks; map queries to intents (informational, commercial, transactional).
Mark “rising queries” (growing impressions) to prioritize fresh internal links—faster indexation and better crawl allocation help you capture momentum (indexation insights).
Define or refine topic clusters and hub pages
Establish a cluster architecture (hub and spokes) that your links will reinforce. If you need a fast framework, adapt our pillar page template and our playbook for automated internal linking across topic clusters.
The 7‑Step AI Internal Linking Workflow (End‑to‑End)
Step 1: Set goals and guardrails
Define anchor style: 60–70% natural/semantic, 20–30% partial match, ≤10% exact match.
Cap links: 3–6 new contextual links per 1,000 words; avoid sitewide injections.
Exclude templates, legal, or utility pages; log all changes and approvers.
Step 2: Collect candidate source and target pages
Sources: pages with traffic, impressions, or strong backlink equity.
Targets: hub pages, revenue pages, orphaned/deep URLs (3+ clicks), and seasonal content.
Score each URL on traffic, conversions, click depth, and topical fit.
Step 3: Use LLM prompts to propose link pairs
Feed structured inputs (URL, headings, excerpt) to get source → target recommendations with anchors.
Ask for the exact paragraph/sentence where the link should live, not just the page pair.
Generate multiple anchor variants to prevent repetition.
Step 4: Validate anchors and on‑page context
Reject anchors that are over‑optimized or duplicate an existing in‑page link.
Require topical proximity: anchor must reference entities found on the target page.
Check for 3xx/4xx targets; avoid chains. Fix or replace before publishing.
Step 5: Prioritize by impact
Score each suggestion on:
Source strength: traffic/backlinks.
Target opportunity: query impressions, revenue potential.
Depth reduction: moving a target from 4+ clicks to ≤3.
Topical fit: embeddings similarity score.
Teams report 12–18% average ranking lifts for optimized pages within weeks when internal linking and on‑page fixes are deployed together (benchmark).
Step 6: Implement safely in your CMS
Ship in small batches with change logs and a rollback plan.
Prefer contextual links in body paragraphs over sidebars or footers.
Tag links for analytics (event category: internal‑link) to measure assisted clicks.
Step 7: QA and measure results
Re‑crawl to confirm links render on the live DOM and aren’t blocked by JS.
Track click depth, internal link counts, and indexation speed in GSC.
Annotate deploy dates; compare pre/post impressions and average position.
Quick win: Strengthen links from your top three traffic pages to your top three money pages. It’s fast, safe, and compounds over time.
Want the content that makes internal links work even harder? Use SEOsolved to generate hub/spoke articles and then run this workflow. Stat Ranking Today.
Prompt Templates for Automated Internal Linking Suggestions
Anchors that avoid over‑optimization
Copy, paste, and adapt:
Act as an SEO editor. You will propose internal links that read naturally.
Inputs:
- Source URL, title, H1, key paragraphs
- Candidate target URLs with titles, entities, and summaries
Rules:
- 60-70% semantic anchors, 20-30% partial match, <=10% exact match
- No duplicate anchors on a page; avoid sitewide patterns
- Suggest 3 anchor variations per pair
Output (JSON): [{"source":"","target":"","anchor_options":["","",""],"place_after_sentence":"exact text"}]Finding the best paragraph for link placement
Identify the single best paragraph for a contextual link.
Criteria:
- The paragraph mentions the same entities as the target page
- The anchor should be 2-6 words, grammatically natural
Return JSON with exact paragraph index and the sentence to link.
Output: {"source":"","target":"","paragraph_index":2,"sentence":""}Producing a clean JSON output for bulk editing
Standardize outputs so you can paste into a sheet or post to an API.
[
{
"source_url": "https://example.com/blog/source",
"target_url": "https://example.com/blog/target",
"anchor": "semantic anchor",
"placement": {
"paragraph_index": 3,
"after_text": "full sentence text to match"
},
"notes": "avoid exact match; first occurrence only"
}
]For more AI workflows beyond linking, check out machine learning for SEO.
Choosing Internal Linking Tools and AI Stack
Crawl and audit layer
Requirements: large‑site crawling, internal links report, click‑depth, exports, JS rendering.
Outputs you need: URL list, headings, word count, status code, canonical, current internal links, orphan report.
Vector search and similarity layer
Use embeddings to measure semantic similarity between source passages and target pages.
Store vectors in a lightweight index so you can re‑score as content changes.
AI clustering often improves topical match rates by 30–40% in competitive niches (benchmark).
CMS and workflow layer
Staging preview, approvals, change logs, and rollback are non‑negotiable.
Prefer componentized link inserts and avoid editing raw HTML per page.
Choosing tools? See our AI SEO platform buyer’s guide.
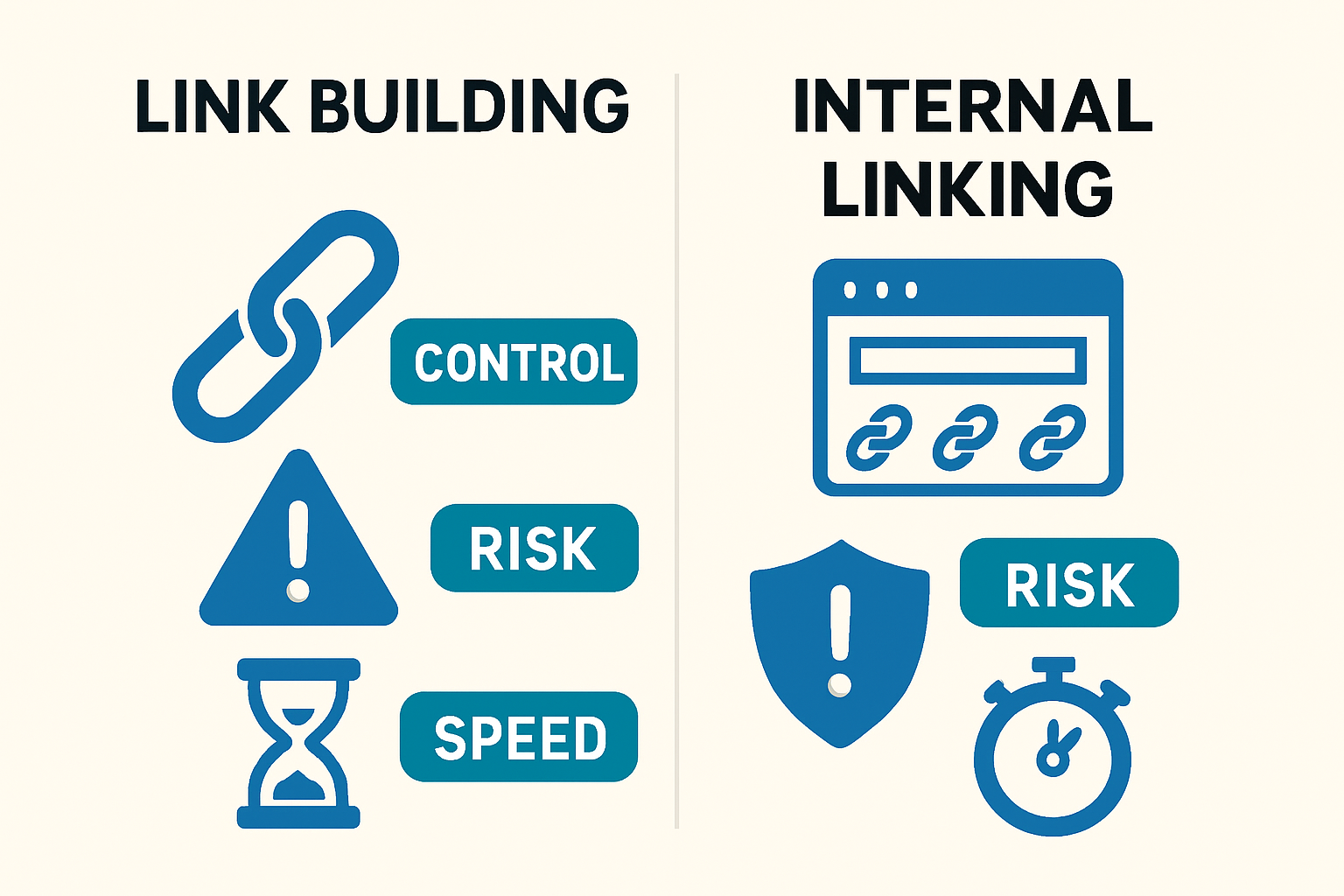
Automated Link Building vs. Internal Linking
Both have a place, but only one is under your full control. Strengthen internal links first to capture quick, low‑risk gains (why it matters).
Factor | Automated Link Building | Internal Linking |
|---|---|---|
Control | Low; external sites decide | High; fully owned |
Risk | Potential spam/footprints | Low when contextual |
Speed | Slow outreach cycles | Fast; batch deploys |
Predictability | Variable | High with guardrails |
Why internal links are a low‑risk growth lever
They’re within your control and reversible.
They directly improve crawl paths and intent alignment.
They compound with each new piece of content.
Avoid automation footprints and anchor spam
Rotate anchor types, avoid repeating the same phrase across multiple pages.
Keep links contextual; skip boilerplate sitewide blocks.
Run periodic audits to remove outdated or redirected targets.
Prioritization Framework for Maximum Impact
Target money pages, hubs, and seasonal content
Support revenue pages from high‑traffic informational articles.
Reinforce hub pages with spokes to establish topical authority.
Boost seasonal content 4–6 weeks before peak demand.
Fix orphaned and deep pages first
Reduce click depth to 2–3 for high‑value pages—this improves crawl frequency and indexation speed (evidence).
Add multiple contextual links from relevant, high‑traffic sources.
Monitor the GSC internal links report and crawl stats for movement.
Implementation Patterns by CMS
WordPress: Blocks, templates, and reusable components
Create a reusable block for “Contextual Link” that enforces rel, tracking, and style.
Use template parts to add optional in‑content link slots without editing each post.
Pair with a quality pillar/hub template to scale structure.
Shopify: Theme sections and content snippets
Add a rich text section in product and blog templates for editorial links.
Use metafields to store curated internal targets per collection or product type.
Avoid sitewide footers stuffed with keyword links.
Headless/Custom: Components and PR workflows
Build a “LinkSuggestion” component that accepts URL, anchor, and placement props.
Submit internal link batches via pull requests for code review and QA.
Re‑crawl staging to catch rendering issues before merge.
Measuring Results: Metrics and Dashboards
Click‑depth and internal PageRank simulations
Track average click depth for priority pages; aim for 2–3 clicks from the homepage.
Run internal PageRank or link score simulations to spot equity bottlenecks.
GSC internal links and query movement
Use the GSC internal links report to confirm increases for target URLs.
Monitor query impressions and average position post‑deploy; annotate changes.
Before/after tests and annotation
Batch tests: deploy to a subset and compare KPIs to untouched controls.
Track indexation speed for new pages—faster transition from “Discovered” to “Indexed” indicates effective internal linking.
Reduced bounce rates often follow early contextual links that route users deeper (behavioral impact).
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Over‑optimized, repetitive anchors
Rotate anchors; lean on semantic phrases and partial matches.
Cap exact‑match anchors and avoid repeating the same anchor across many pages.
Sitewide links and navigation bloat
Favor in‑content links over boilerplate blocks.
Keep menus lean; too many template links dilute equity to low‑priority pages.
Redirect chains and broken links
Disallow 3xx chains; update to the final 200 URL.
Audit for 404s after every batch deploy.
Where SEOsolved Fits in Your AI Internal Linking System
Use SEOsolved to build clusters and publish high‑quality articles
SEOsolved analyzes competitors, surfaces hundreds of ranking keywords, and generates SEO‑optimized articles with credible sources in ~30 minutes. Strong clusters plus clean internal linking accelerate authority. Teams using AI‑assisted content strategies report faster production and higher CTRs (user benchmarks) and improved content efficiency (case insights).
Feed the content roadmap into your AI linking prompts
Map SEOsolved hub/spoke outputs to your linking targets and anchor themes. Then use the prompts above to scale contextual links that reinforce clusters. For deeper tactics on cluster execution, see our guide on automating links inside topic clusters.
Recommended cadence: publish → link → measure → iterate
Publish 4–8 optimized posts per month via SEOsolved.
Run link suggestions weekly; deploy in batches.
Measure and prune monthly; repeat.
Ready to pair content with smart internal links? Stat Ranking Today.
Mini Case Study: 100‑URL Site to +25% Organic Clicks
Week 1: Inventory and clustering
Crawl 100 URLs; export headings and current internal links.
Cluster into 10 hubs and 40 spokes; identify 15 orphaned or deep pages.
Draft hub outlines using our pillar framework.
Week 2: AI suggestions and review
Generate 200 link suggestions with anchor variants; approve 120 after QA.
Reject 20 for over‑optimization; rephrase to semantic anchors.
Map 10 links specifically to reduce click depth on high‑value deep pages.
Week 3: Implementation and monitoring
Deploy in two batches; re‑crawl to validate live links and status codes.
Watch GSC internal links counts and query movement; annotate changes.
Result (60–90 days): +25% organic clicks, faster indexation for new posts, and improved time‑on‑page from better in‑content routing—consistent with industry findings on internal links’ impact on indexation and engagement (evidence).
Checklist, Templates, and Next Steps
Export URL inventory with headings, word count, click depth, and internal links.
Map queries and clusters; define hubs/spokes and exclusions.
Run the prompt templates; require paragraph‑level placement.
QA anchors; prioritize by source strength, target value, and depth reduction.
Ship in batches; log and annotate; measure and iterate.
Download: Prompt and JSON schema templates
Copy the prompts and JSON examples above into your playbook. Standardize outputs now so future batches take minutes, not hours.
Call to action: Pair content with smart internal links
Use SEOsolved to generate authoritative clusters, then apply this AI internal linking workflow to route equity and intent where it matters most. Stat Ranking Today.
AI Internal Linking: FAQ
How many internal links per page is safe?
As a rule of thumb, add 3–6 contextual links per 1,000 words. Prioritize in‑content links over template links and avoid repeating the same anchor.
What anchors should I use for internal links?
Aim for 60–70% natural/semantic anchors, 20–30% partial match, and under 10% exact match to avoid over‑optimization and keep links helpful.
How do I pick source and target pages?
Choose sources with traffic or backlinks, and targets with revenue potential, rising impressions, or excessive click depth (3+). Reinforce hubs first.
Do internal links help indexation speed?
Yes. Strong internal links shorten click paths, guide crawlers, and often move pages from Discovered to Indexed faster, especially for new or updated content.
Is automated link building necessary?
Not to start. Internal linking is safer, faster, and fully controllable. Build strong internal pathways first; then pursue high‑quality external links
