Your organic growth in 2026 will be won or lost on technical execution. This playbook shows exactly how to fix crawl, render, index, speed, and JavaScript challenges—and pair them with a content engine that compounds.
We’ll cover the full technical SEO lifecycle, HTML best practices, Core Web Vitals, JavaScript frameworks, structured data, CMS-specific setups, software and automation, resourcing, measurement, and a 90‑day plan. By the end, you’ll have a prioritized roadmap you can ship this quarter.
Why Technical SEO Still Wins in 2026
Technical SEO aligns site architecture, crawlability, renderability, and performance with your business goals. Without it, even great content stays invisible. With it, search engines can find, understand, and rank your pages consistently.
In a world of multi-surface results (AI Overviews, Discover, video, and classic blue links), infrastructure quality decides who shows up first across surfaces. As industry experts note, optimizing for multi-modal visibility is now table stakes—not optional. Strong technical SEO optimization increases crawl efficiency, stabilizes rankings, and improves conversion by reducing UX friction.
- Search visibility: Clean signals and fast pages win more impressions and richer features.
- Crawlability: Open the right doors and conserve crawl budget for money pages.
- Durability: Fewer regressions during releases; faster recovery when issues occur.
Definition for featured snippets: Technical SEO is the practice of optimizing a site’s infrastructure so search engines can crawl, render, index, and rank content reliably and efficiently.
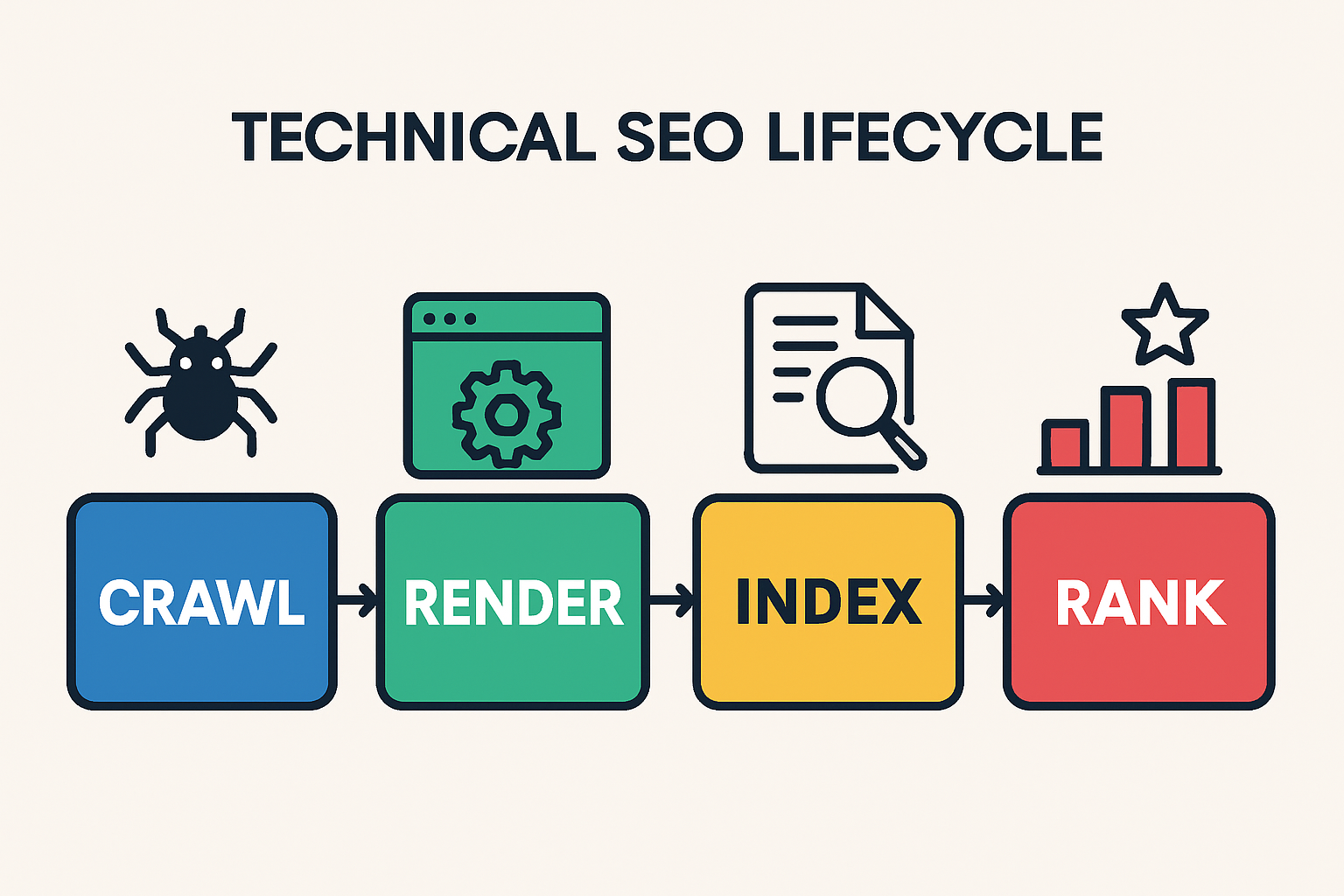
Technical SEO Foundations: Crawl, Render, Index
Think of Google’s pipeline as three non‑negotiable stages. Prioritize fixes in this order to avoid wasted effort.
- Crawl: Bots discover URLs via sitemaps, internal links, and backlinks, then request your HTML.
- Render: The page is processed; JavaScript executes; the DOM is built and content becomes visible.
- Index: Google stores page content and signals; the URL becomes eligible to rank.
Note that indexing can lag crawling by days or weeks on large sites. Use this lifecycle to triage: unblock crawl first, then fix rendering, then refine indexation.
Crawlability: robots.txt, XML sitemaps, and internal links
Start by making sure bots can reach your valuable URLs and ignore junk. The triad that moves the needle:
- robots.txt: Allow critical paths; disallow admin, faceted traps, and infinite calendars. Don’t block assets required to render pages.
- XML sitemaps: Submit clean, canonical URLs only; segment by type (blog, product, category) to monitor coverage precisely.
- Internal linking: Distribute PageRank to revenue pages from navs, hubs, and relevant articles. Automate guardrails to prevent orphaning.
Pro tip: Use segmented sitemaps plus crawl diffs to spot sudden drops in discoverability. To scale internal linking, see our guide on automated internal linking for topic clusters.
Renderability: handling JS, pre-rendering, and dynamic content
JavaScript-heavy pages require extra care. When the browser (or Google) loads your app, it must download and execute JS before content appears. On large sites, this can slow indexing or hide content entirely if scripts fail. Prefer server-side rendering (SSR), static site generation (SSG), or hybrid approaches for critical pages. If you must ship client-side rendering (CSR), provide fallbacks and ensure links are true anchors with crawlable hrefs.
- Pre-render key templates or use dynamic rendering to serve HTML to bots for complex widgets.
- Confirm what Google sees using Chrome DevTools and URL Inspection; compare raw HTML vs. rendered HTML.
- Expose navigation and product lists as actual links, not onclick handlers.
Indexation control: canonicals, noindex, and duplicates
Manage what gets into the index and consolidate duplicates to concentrate authority:
- Canonical tags: Point variants to a single source of truth. Ensure canonicalized URLs are self-referential and indexable.
- Noindex: Keep thin search results, internal search pages, and uncontrolled parameters out of the index.
- Parameter handling: Append tracking parameters via JS or route them server-side; avoid creating infinite URL variants.
Featured snippet quick list: Indexation rules to remember — 1) One canonical per cluster, 2) Noindex thin/duplicate pages, 3) Block crawl of traps, not value pages, 4) Keep sitemaps pristine.
HTML SEO Best Practices That Move the Needle
Great HTML clarifies meaning for both crawlers and humans. These HTML SEO best practices upgrade relevance and click-through at scale.
Semantic structure: headings, lists, alt text, and links
- Headings: Use a logical H1–H2–H3 hierarchy; one H1 per page; avoid skipping levels.
- Lists and tables: Summarize steps and comparisons to capture featured snippets and improve scannability.
- Alt attributes: Write descriptive alt text for images; treat it as accessibility-first, SEO-second.
- Anchors: Use concise, descriptive anchor text that matches the destination’s intent.
Build topical authority with tight clusters and internal links. For a deeper approach, see Semantic SEO: The Fast Track to Unshakable Authority.
Metadata mastery: titles, metas, and structured snippets
- Title tags: Lead with the primary value; keep under ~60 characters; include differentiators (2026, pricing, templates).
- Meta descriptions: 150–160 characters; promise the outcome; include a CTA.
- Open Graph & Twitter Cards: Control previews to boost CTR on social and chat surfaces.
- Breadcrumbs & schema: Clarify site structure for users and crawlers.
Site Performance and Server SEO
Speed is a feature. It improves UX, conversion, and crawling efficiency. Treat performance as a product with budgets, monitoring, and regression tests.
Core Web Vitals in 2026: LCP, INP, CLS
Focus on the three metrics Google uses most: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), Interaction to Next Paint (INP), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). Practical tips:
- LCP: Serve hero images fast via preload, responsive sizes, and CDNs; minimize render-blocking resources.
- INP: Reduce main-thread work; split bundles; defer non-critical JS; use web workers for heavy logic.
- CLS: Reserve space with width/height; avoid layout-janking ads; load fonts with swap.
Server SEO: hosting, HTTP/2–3, caching, CDN, compression
- Protocols: Enable HTTP/2 or HTTP/3 for multiplexing and lower latency.
- Caching: Set strong caching headers; use stale-while-revalidate; cache HTML for anonymous traffic.
- CDN: Put a CDN close to users; use edge functions for personalization without blocking TTFB.
- Compression: Prefer Brotli for text; audit bundles and images regularly.
- Logging: Keep bot logs to analyze crawl behavior and waste.
Security, redirects, and HTTPS best practices
- HTTPS everywhere; enforce with HSTS; include subdomains where relevant.
- Redirects: Use 301s for permanents; avoid chains and loops; update internal links to target URLs.
- Security headers: Content-Security-Policy, X-Content-Type-Options, and more to protect users and trust signals.
JavaScript, AJAX, and SEO for Web Applications
SPAs and modern frameworks can rank extremely well—when you choose the right rendering strategy and expose crawlable states.
SEO for web applications: SSR, hydration, and routing
Pick the rendering model that fits your content, update frequency, and infrastructure:
| Model | Best for | Pros | Watch outs |
|---|---|---|---|
| SSG | Docs, blogs, marketing pages | Instant HTML; great CWV; easy caching | Build times for large sites; ISR/hybrid may be needed |
| SSR | Dynamic catalogs, geo content | Fresh server-rendered HTML; crawl-friendly | Compute cost; cache strategy matters |
| ISR/Hybrid | Large sites with frequent updates | Rebuild per-path; balances freshness and speed | Cache invalidation complexity |
| CSR | Web apps where SEO is secondary | Rich interactivity; simple hosting | Requires extra work to index; risk of empty HTML |
AJAX and SEO: progressive enhancement and crawlable states
- Progressive enhancement: Content and links render without JS; JS upgrades UX.
- Stateful URLs: Use pushState to map filters/sorts to clean URLs that load server-side too.
- Pagination: Provide real links; keep params tidy; avoid infinite scroll without pagination.
JavaScript dynamic content: rendering strategies that index
- Pre-render or dynamic render for bots when components hide critical text or links.
- Edge rendering for geo, A/B, and personalization without harming TTFB.
- Always validate with Chrome DevTools and URL Inspection to confirm rendered DOM matches expectations.
SEO in software products: docs, changelogs, and SDKs
Product surfaces are growth engines. Make them discoverable:
- Developer docs: Structure by tasks; add code samples; use schema; link across SDKs.
- API references: One endpoint per URL; include examples; add breadcrumb and FAQ schema where valid.
- Changelogs: Summaries per release; link to docs; tag versions; interlink related guides.
- Information architecture: Use hubs for languages, frameworks, and use cases.
Structured Data and Rich Results
Schema helps machines understand entities, relationships, and intent. Map business goals to the highest-impact types, then validate continuously.
Must-have schema: Organization, Product, FAQ, HowTo
- Organization: Reinforce brand identity (logo, sameAs) and eligibility for knowledge panels.
- Product: Price, availability, and reviews for richer commerce listings.
- FAQ: Clarify common questions; reduce friction and support self-serve.
- HowTo: Step-by-step tasks; capture visual rich results where relevant.
Validation, monitoring, and deprecation-proofing
- Validate with Rich Results Test; fix errors and warnings before deploying broadly.
- Monitor Search Console Enhancements for coverage and changes in support.
- Version schema patterns; keep an eye on deprecations and update templates proactively.
CMS-specific Technical SEO: WordPress, Wix, Joomla
Each CMS has guardrails and limitations. Configure the fundamentals first, then optimize for performance and scale.
WordPress: settings, performance, and plugins
- Permalinks: Use post name; avoid date slugs unless news-focused.
- XML sitemaps: Ensure only canonical, indexable URLs appear; exclude tags if thin.
- Media: Compress, lazy-load, and generate WebP; add descriptive alt attributes.
- Performance: Page caching + object caching; limit plugins; defer JS; host fonts locally.
- WordPress SEO optimization plugin: Choose a stable, well-supported option; enable breadcrumbs, schema, and redirects thoughtfully.
When to engage a WordPress SEO agency
Bring in a WordPress SEO agency when migrations, complex theme refactors, or internationalization exceed in-house bandwidth. Agencies accelerate QA, reduce migration risk, and formalize redirects and schema rollouts. For agency-side execution frameworks, see SEO for Agencies: 2026 Playbook.
Wix search engine optimization: what to configure
- Set custom meta titles/descriptions; configure structured data where Wix allows.
- Use built-in redirects for URL changes; keep sitemap clean.
- Control auto-generated pages; prevent thin tag archives from indexing.
Joomla SEO optimization: URLs, metadata, and caching
- SEF URLs: Enable friendly URLs and URL rewriting; keep slugs concise.
- Metadata: Ensure titles and descriptions are editable per article and menu item.
- Caching & compression: Use Joomla caching, CDN, and Gzip/Brotli for speed.
Technical SEO Software, Audits, and Automation
Design recurring audits that cover crawls, logs, and CI checks. Your stack should reveal what bots see and stop regressions before deploy.
Crawlers and log analysis: see what bots see
- Full crawls + diffs: Track changes to titles, canonicals, robots, noindex, and links across releases.
- Log file analysis: Identify waste (parameters, faceted loops) and orphaned pages; re-route crawl budget.
- Render testing: Fetch & render key templates to validate JS and navigation exposure.
Your 2026 technical SEO software stack
- Crawling & rendering: Enterprise crawler with JS rendering, scheduling, and API.
- Performance: Synthetic + RUM for CWV tracking and alerting.
- Monitoring: Uptime, redirect checks, robots/headers diffs; alert on changes.
- Reporting: Dashboards that segment by template and directory.
Choosing tools? Benchmark options against the best SEO audit tools for your use case.
Automation in CI CD: guardrails for every release
- Pre-merge tests for titles, canonicals, robots, hreflang, structured data, and redirects.
- Block deploy if robots.txt, meta robots, or status codes change unexpectedly.
- Snapshot CWV and key page HTML; diff against baselines.
Build vs Buy: Technical SEO Agencies vs In-House
Pick the model that maximizes speed-to-value, not just hourly cost. Complex stacks and migrations often benefit from specialized partners; steady-state operations fit strong in-house teams.
When to hire technical SEO agencies
- High-risk site migration or replatforming
- JS-heavy SPAs with rendering challenges
- International SEO with hreflang and localization
- Understaffed engineering/design bandwidth
Vetting questions and SLAs that protect outcomes
- What’s your technical roadmap for our templates and stack?
- Show example QA processes for redirects, canonicals, and schema.
- Which SLAs cover reporting cadence, response time, and rollback support?
- How do you measure impact on revenue, not just traffic?
Align Technical SEO with Content Velocity
Technical excellence amplifies content, but it cannot replace it. You need a predictable pipeline of useful, search-focused articles that publish weekly and capture demand as it emerges.
Use SEOsolved to accelerate content strategy and output
SEOsolved automates the heavy lifting so your team can ship faster:
- Competitor analysis: See what topics and formats are winning now.
- Keyword discovery: Uncover hundreds of relevant opportunities by intent and difficulty.
- Content roadmap: A prioritized plan mapped to your buyers and templates.
- AI content generation: High-quality, SEO-optimized drafts with credible sources—ready in about 30 minutes.
Example: A B2B startup with a lean team used SEOsolved to identify overlooked, bottom‑funnel keywords and publish consistently without adding headcount—freeing devs to focus on performance and schema.
Workflow: technical fixes plus a scalable content pipeline
- Weekly: Ship technical fixes (CWV, links, redirects); publish 2–4 articles from the roadmap.
- Monthly: Review coverage and rankings; expand clusters with internal links and new briefs.
- Quarterly: Refresh top performers; add schema; roll out new templates.
For briefing discipline that speeds execution, try our guide to AI content briefs.
Measurement and Ongoing Improvement
Tie technical metrics to outcomes. Dashboards and alerts should surface crawl health, index coverage, and revenue—not just vanity scores.
Core KPIs: crawl health, index coverage, CWV, and revenue
- Crawl stats: Requests by section; bot types; response codes; timeouts.
- Index coverage: Indexed vs. submitted; canonical mismatches; soft 404s.
- Core Web Vitals: LCP/INP/CLS pass rates by template and device.
- Revenue attribution: Page and template-level assisted and direct conversions.
Diagnostics: anomaly detection and rollback plans
- Alert on spikes in noindex, redirect chains, 404s, or robots.txt changes.
- Detect traffic anomalies by segment; compare to deploy timelines.
- Prepare rollback plans for template regressions and deployment failures.
Refresh content strategically. A proven approach: Optimizations (small on-page tweaks), Upgrades (refresh sections, stats), and Rewrites (rethink the angle when intent has shifted).
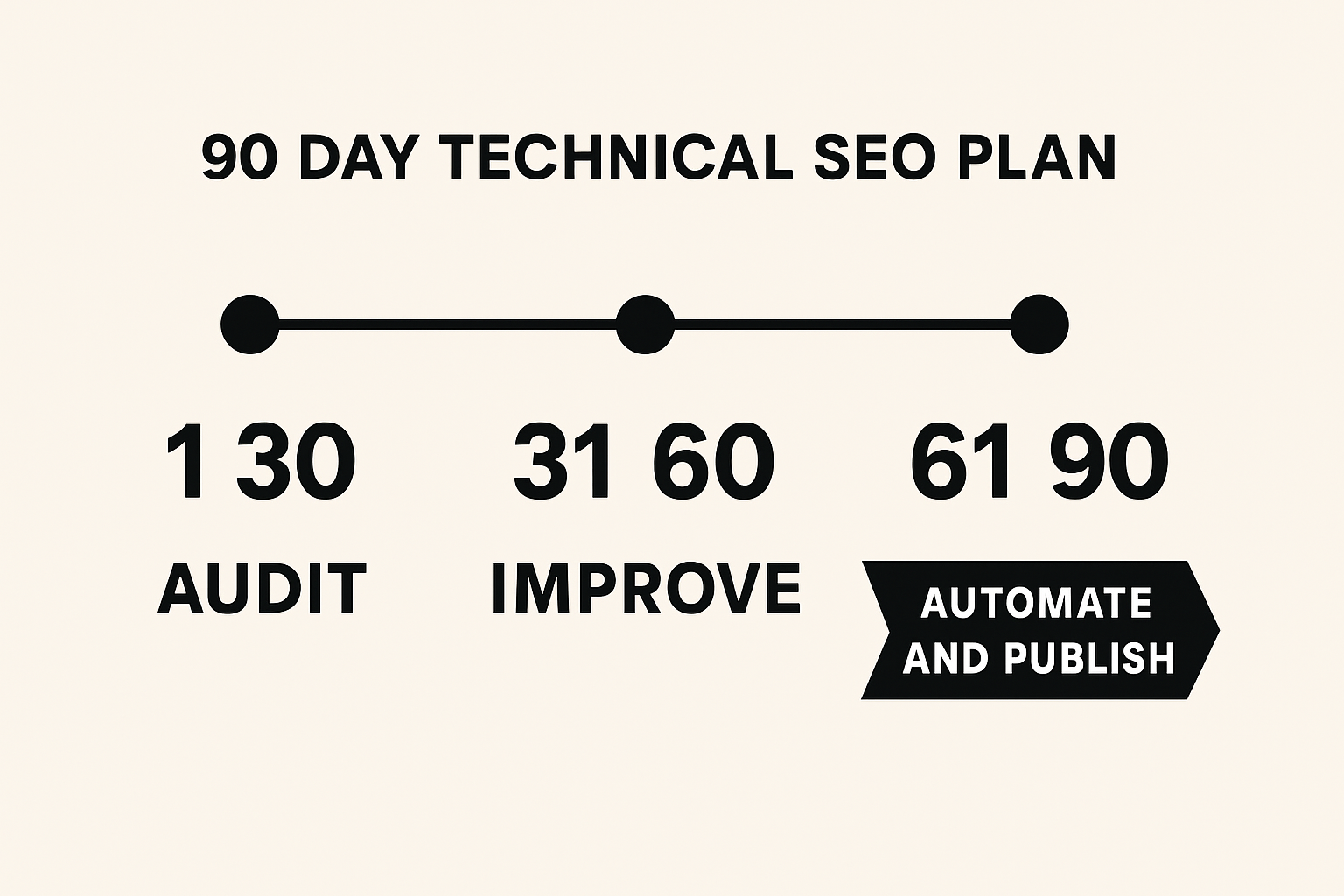
90-Day Technical SEO Roadmap
Here’s a pragmatic plan that balances speed with durability. Use it as a template and adjust by site complexity.
Days 1–30: Audit depth and quick wins
- Run a full site audit with JS rendering; fix critical indexation issues.
- Repair internal linking; surface orphan pages; ship XML sitemap fixes.
- Eliminate redirect chains and soft 404s; set correct canonical rules.
- Improve top templates’ titles, metas, and structured data.
Days 31–60: Core improvements and platform hardening
- Ship CWV upgrades (LCP/INP/CLS) and server SEO enhancements (HTTP/2–3, Brotli, CDN).
- Implement Organization/Product/FAQ/HowTo schema at scale.
- Introduce CI checks for robots, canonicals, and redirects.
Days 61–90: Scale, automate, and publish
- Automate technical checks; expand internationalization if relevant.
- Ramp content with SEOsolved to sustain momentum.
- Review KPIs; lock in maintenance cadences and alerting.
FAQ
What is technical SEO?
It’s the discipline of optimizing your site’s infrastructure so search engines can crawl, render, index, and rank content reliably.
How long does it take for pages to index?
Crawling can happen quickly, but indexing may take days or weeks depending on site scale, crawl demand, and quality signals.
Do JavaScript frameworks hurt SEO?
No—if you use SSR/SSG/ISR or provide crawlable fallbacks, expose links, and validate rendered HTML for key templates.
Which Core Web Vitals matter most in 2026?
LCP, INP, and CLS. Aim to pass thresholds across device types and key templates.
When should I hire a technical SEO agency?
For high-risk migrations, JS-heavy stacks, or international SEO when in-house bandwidth or expertise is limited.
References and Further Reading
- Technical SEO lifecycle and rendering realities from Search Engine Land
- Render diagnostics with Chrome DevTools guidance by Christopher S. Penn
- Why technical SEO unlocks crawling, rendering, indexing, and ranking (CXL, Adonis Media)
- Multi-surface SEO priorities for 2026 (Search Engine Journal)
- Content refresh methodology and semantic relevance (Backlinko)
- Client vs. server rendering tradeoffs (Wix resource)
